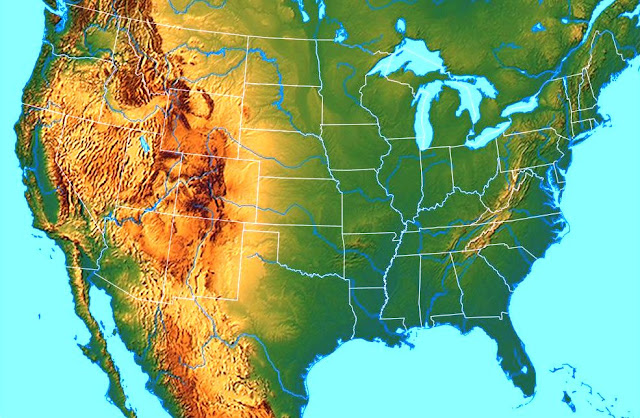
- Introduction
- U.S.A. Borders
- Physiographic Characteristics
GEOGRAPHY OF U.S.A. | Introduction
Being one of the largest countries in the world, United States has a diverse geography. Besides, presence of the North Pole state of Alaska, Island state of Hawaii and various territories throughout the globe makes U.S. geographically the most diverse country in the world.
U.S. has the fourth-longest river, second-largest lake, ninth-largest cold winter desert and tenth-largest subtropical desert in the world. As a matter of fact the country has a vast reserve of natural resources and minerals.
In geographical sense the term United States or U.S. generally mentions contiguous United States, Alaska, Hawaii, five insular territories and minor outlying processions. The five insular territories of the U.S. or inhabited territories are:-- Puerto Rico
- Northern Mariana Island
- Guam
- American Samoa and
- U.S. Virgin Islands
Minor outlying processions of U.S.A. refers to a group of 8 United States Minor Outlying Islands; consist of Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Palmyra Atoll, Wake Atoll and Navassa Island. Except Navassa Island, which lies in the Caribbean Sea; all other islands are situated in the Pacific Ocean.
GEOGRAPHY OF U.S.A. | U.S.A. Borders
Due to its vastness and scattered geography, the United States has a peculiar setup of borders, which cannot be understand with a short phase of words unlike any other country in the world.The District of Columbia and 48 states of U.S. mainland, which is known as Contiguous United States shares it’s border with Canada in north and Mexico in south. In east Cuba, Bahamas and other countries in the Atlantic Ocean shares their maritime borders with United States. On west, it is Pacific Ocean. The borders between Canada and US is the longest bi-national land border in the world.
But the border of U.S.A. is a little bit different from that of Contiguous United States due to the presence of Alaska. From that point of view USA shares its land border with Russia in north, in addition with Canada on north and south. Thus, Continental U.S.A. has a maritime border with Russia in west.
Other countries that shares maritime borders with USA apart from Russia, Canada, Mexico and Cuba are:
Colombia, Jamaica, Nicaragua, Haiti, Bahamas, Dominican Republic, Japan, Kiribati, Marshall Island, Federated States of Micronesia, Netherlands, Samoa, Tonga, Venezuela, United Kingdom (Anguilla, British Virgin Islands) and New Zealand (Cook Island, Niue, Tokelau).
The presence of US directly controlled territories globally, makes the border of the USA a far more critical subject. So, the above mentioned border(s) is generally accepted to define US borders.
Though US has borders unlike any other nation in the world, it too has border disputes like most of the nations. Apart from disputes with Cuba, Haiti, Colombia, Jamaica and Nicaragua; U.S. Canada Border also has several issues to be solved.
GEOGRAPHY OF U.S.A. | Physiographic Characteristics of the United States
In the broadest sense the geography of U.S.A. can be divided into three parts, Eastern USA, Central U.S.A. and Western USA. These major divisions are categorized into some major geographical regions.Eastern U.S.A.
Major Eastern U.S. Geographic Regions: (i) Northeast (ii) Southeast.Northeast U.S.A. States and Territories: Maine, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire, Vermont, New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands.
Southeast U.S.A. States: West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Arkansas, Louisiana, Florida.Geographic Features of East United States
- The varied topography is extended from the Texas border to Maine.
- The Eastern Seaboard is separated by the Appalachian Mountains from the Great Lakes and the Mississippi Basin, form a line of low mountains. Offshore Islands dot the Atlantic and Gulf coasts.
- This plain of Florida Peninsula, Atlantic and Gulf shores along with barrier islands make up the widest and longest soft white sand beaches in the United States.
- Florida Keys, a coral cay archipelago (string of coral islands) reaches Key West, the southernmost city on the United States mainland.
 |
| A Portion of Florida Keys |
- Areas further inland feature rolling hills, mountains, having a diverse collection of temperate and subtropical moist and wet forests; along with sand-hills in parts of interior Florida and South Carolina.
- New England has rocky seacoasts, rugged mountains and valleys full of rivers and streams. The New England Fifty Finest includes a group of mountains ranged between 1,820 ft/ 895 m (Moxie Mountain) and 6,288 ft/ 1,917 m (Mount Washington) in height.
- The southeast United States is stretched from the Ohio River on south. Southeast includes a variety of warm temperate and subtropical moist and wet forests. The region also has warm temperate and subtropical dry forests nearer the Great Plains in the west of the region.
- A number of tropical isles in the northeastern Caribbean Sea are encompassed due to the presence of the territories of Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands.
Central U.S.A.
Major Central U.S. Geographic Regions: (i) Midwest (ii) Southwest.Midwest U.S.A. States: Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, Illinois, Missouri, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota.
Southwest U.S.A. States: Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona.Geographic Features of Central United States
- There located five Great Lakes in the north-central portion of the country, of which only Lake Michigan situated entirely within United States, other four of them forming part of the border with Canada.
- Lush Mississippi River basin and two large eastern tributaries, the Ohio River and the Tennessee River are situated west of the Appalachians.
- The Midwest along with Ohio and Tennessee Valleys consist largely of rolling hills, interior highlands and small mountains. The jungly marsh and swampland near the Ohio River, stretching south to the Gulf Coast gradually becomes productive farmland.
- The Midwest has a vast amount of cave systems.
- The Great Plains lie west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains. The region grows a large portion of the country's agricultural products.
- From tallgrass prairie in the eastern plains to shortgrass steppe in the western High Plains, once the Great Plains were noted for their extensive grasslands, before their gradual conversion into farmland.
 |
| Landscape of the Great Plains near Rocky Mountains |
- Elevation rises gradually from less than a few hundred feet near the Mississippi River to more than a mile high in the High Plains.
- The Ozark and Ouachita Mountains forms the U.S. Interior Highlands, the only major mountainous region between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains. This area breaks the generally low relief of the plains between Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains.
Western U.S.A.
Major Western U.S. Geographic Regions: (i) West (ii) State of Alaska (iii) Pacific Islands.West U.S.A. States and Territories: Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, Idaho, Washington, Oregon, Utah, Nevada, California, Alaska, Hawaii, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, American Samoa.
Geographic Features of Western U.S.A. States
- The Great Plains come to an abrupt end at the Rocky Mountains, entering from Canada and stretching nearly to Mexico, form a large portion of the Western U.S.
- The Rocky Mountains is the highest region of the United States by average elevation.
- The Rocky Mountains has fairly mild slopes and wider peaks compared to some of the other great mountain ranges. However there are a few exceptions, such as the Teton Mountains in Wyoming and the Sawatch Range in Colorado.
- The highest peaks of the Rockies are found in Colorado, containing Mount Elbert (14,440 ft/4,400 m) as the tallest peak.
- Although the Rockies are generally described as continuous and solid mountain range, it is broken up into a number of smaller, intermittent mountain ranges, forming a large series of basins and valleys.
- A large, arid desert (Intermontane Plateaus a.k.a. the Intermountain) lies between the Rockies on east and the Cascades and Sierra Nevada ranges on west. Consists of salt flats, drainage basins, and many small north–south mountain ranges, the large southern portion of Intermontane Plateaus is known as the Great Basin.
- The Southwest of western US. is predominantly a low-lying desert region. A portion of it, centered around the Four Corners region is known as the Colorado Plateau.
- Containing some natural wonder, such as Grand Canyon, Arches, Mesa Verde and Bryce Canyon among others; Colorado Plateau is known for delivering some of the most spectacular scenery in the world.
- Eastern Washington, western Idaho and northeast Oregon and the Snake River Plain in Southern Idaho are some smaller but important Intermontane areas that situated on Columbia Plateau.
- The Intermontane Plateaus come to an end with Cascade Range and the Sierra Nevada starts.
- The Cascades includes largely intermittent, many prominently rising volcanic mountains.
- Further south to the Cascades, the Sierra Nevada is a high, rugged, and dense mountain range.
- Between the boundary of California's Inyo and Tulare counties, Sierra Nevada contains Mount Whitney (14,505 ft or 4,421 m), the highest point in the contiguous United States.
- Mount Whitney is located at just 84.6 mi (136.2 km) west-northwest to the lowest point in the continent of North America. Badwater Basin in Death Valley National Park at 279 ft or 85 m below sea level is the lowest point of USA as well as North America.
- The areas of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada also offer some spectacular natural scenery containing national parks, such as Yosemite and Mount Rainier.
- West of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada there lies Pacific Coast with a series of valleys and low mountain ranges. The Central Valley in California and the Willamette Valley in Oregon are the most prominent. The series of low mountain ranges is known as the Pacific Coast Ranges.
 |
| A dramatic landscape of Alaska |
- With tall, prominent mountain ranges rise up sharply from broad, flat tundra plains; Alaska creates some of the most dramatic geographic landscape. Alaska is home not only to Denali, the highest mountain peak in the US, but also numerous other magnificent peaks.
- The island states of Hawaii, also the southernmost U.S. sate and the only state outside the continent; in the Pacific Ocean, is a chain of tropical, volcanic islands. The other islands off the south and southwest coast too have many volcanoes.
- The territories of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, In Pacific Ocean occupy the limestone and volcanic isles of the Mariana archipelago. On the other hand American Samoa, in the eastern part of the Samoan Islands chain encompasses volcanic peaks and coral atolls.
- American Samoa is the only populated U.S. territory in the southern hemisphere.
 |
Kīlauea, Hawaii is one of the most dangerous volcanoes in US Courtesy: The West Hawaii Today |
- Anderson, Ewan W. (2003). International Boundaries: A Geopolitical Atlas. Routledge: New York. ISBN 9781579583750; OCLC 54061586.
- Charney, Jonathan I., David A. Colson, Robert W. Smith. (2005). International Maritime Boundaries, 5 vols. Hotei Publishing: Leiden.
- Brown, Ralph Hall, Historical Geography of the United States, New York : Harcourt, Brace, 1948.
- Physiographic Regions. United States Geological Survey. April 17, 2003.
- Stein, Mark, How the States Got Their Shapes, New York : Smithsonian Books/Collins, 2008. ISBN 978-0-06-143138-8.
Comments
Post a Comment